Fundamental / Technical Analysis - Introduction to Fundamental Analysis in STRATEGIES & PLANS - Fundamental analysis is a method used by investors to identify the intrinsic value of a stock. The current price of ...
-
07-20-2021 10:24 PM

Introduction to Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis is a method used by investors to identify the intrinsic value of a stock. The current price of a stock may not reflect the actual value of the stock. The stock may be overvalued or undervalued in the market. Fundamental analysts study the underlying health of the company in order to find the intrinsic value.
This is done by using various qualitative and quantitative factors such as the company’s revenues, profit margins, return on equity, future growth potential and other metrics. The main purpose of this method is to identify companies that that are fundamentally strong in order to invest in them for the long term.
Importance of Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis helps you in better making an investing decision. Fundamental analysis of stocks helps you determine their fair value. Also, with stock fundamental analysis, you can evaluate the health and performance of any organisation through crucial numbers and major economic indicators.
Fundamental analysis helps you analyse a company’s strength and its ability to beat its competitors. Fundamental analysis of stocks also helps in understanding the business model of a firm and the working of management, essential for making a prudent investment decision.
Tools used in fundamental analysis
Investors use a lot of different tools to determine the actual worth of a stock. This includes:
• Financial statements (balance sheets, income statement, cash flow statement)
• Earnings (quarterly earnings and projected future earnings)
• Financial ratios (Earnings per share, price to earnings ratio, return on equity)
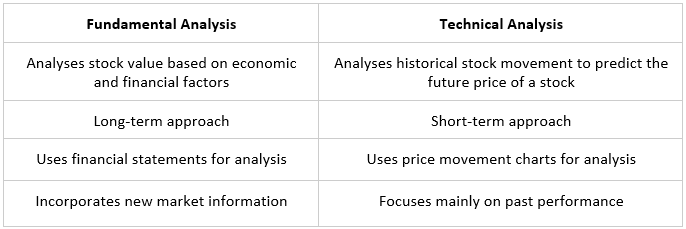
Difference between Fundamental analysis and technical analysis
Types of Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental stock analysis is of two types namely
Quantitative
Quantitative fundamental analysis is related to information that is shown in numbers and amounts. Price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, price-to-book (P/B) ratio and debt/equity ratio are some of the elements of quantitative stocks analysis. This analysis helps you to evaluate investment opportunities such as when to buy and sell securities and involves measuring simple statistical data to complex calculations.
Every company publish Profit & Loss statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow statement periodically. One has to know how to read and understand these statements together to identify the company’s financial situation. Apart from the numbers available on these statements, one need to derive certain ratios so they can be compared with peers to evaluate.
Following are some of the financial ratios used.
• Profitability Ratios
o EBITDA Margin
o Net Profit Margin
• Return Ratios
o Return on Equity
o Return on Capital Employed
• Leverage Ratios
o Debt to Equity
o Interest Coverage
• Liquidity Ratios
o Current Ratio
o Quick Ratio
• Efficiency Ratios
o Assets Turnover
o Inventory Turnover
Qualitative
Qualitative fundamental analysis takes into account information that can’t be expressed in numbers, and it relates to the company itself. It involves information related to management experience and performance, corporate governance, industry and competition and business, among others. While quantitative analysis is more tangible, qualitative is not. Having said that, both have their importance and play a crucial role in the overall process.
It is always better to take top down approach. One need to understand macroeconomics to understand the external factors that can impact business outcomes. Post that, one need to do Industry Analysis to know if the sector will have growth in next decade or so. If one is convinced about a particular sector, then one need to analyse individual players to identify the stock to invest.
Pros and Cons of Fundamental Analysis
The advantages of fundamental analysis are
• Very useful for long term investment approach
• Gives a complete view of financial aspects of a company
The disadvantages of fundamental analysis are
• Financial data is required and cannot be analysed by all
• Involves a lengthy and complex process so patience is key
Conclusion
A bit of research and arithmetic is involved in fundamental analysis. But unlike general perception, it is not used solely by experts and professionals. Every investor can benefit from fundamental analysis in the market.

Similar Threads
-
-
-
-
Fundamental / Technical Analysis
Visitors found this page by searching for:
bse2nse
,
https:bse2nse.comfundamental-technical-analysis10776-introduction-fundamental-analysis.html Tags for this Thread






 Register To Reply
Register To Reply